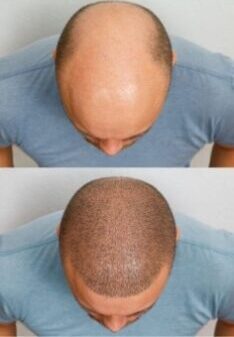
Hair transplantation has appeared as a very desired and highly reliable solution for hair loss. For many, it does not only restore the hair, but there is also the confidence of millions of people around the world. Despite the ongoing advances in technology and techniques, some hair transplants are still unfortunately failing. Understanding the reasons for these failures is essential for anyone who considers this method – especially the surgeon.
Age in Hair Transplants
The main reason for hair transplantation is that they are done on patients who are very young. Important information is the donor area stability. If the donor area is not stable, over time, transplanting hair (caused by the donor area) disappears. The main method that a physician evaluates this stability is to examine the percentage of miniatureization in the donor area compared to complete thick hair. Miniatureization is the thinning and shortening of the hair in response to the hormone (DHT). Eventually this hair disappears. Unfortunately, patients may not show any significant miniature at a young age, although their destination has widespread miniature and baldness. Therefore, assessing a patient for surgery that is very young may have a misconception of the donor and nomination stability.
In our practice, we wait for a person to be at least 25, because it gives us the best opportunity not to perform surgery on a person who may not be a candidate in the future. It 5is just as important that young patients may respond significantly to medical treatment, even if they have significant hair loss.
candidates to be poor
One of the main reasons for the failure to succeed in hair transplantation is the selection of a poor candidate by the physician. In addition to age, not everyone is the ideal candidate for this method. Factors such as hair loss, quality and quantity of donor hair and overall health and scalp (such as extensive sun damage) play an important role in determining the appropriateness. Patients with extensive hair loss and limited donor hair may not reach the desired density. A ethical doctor on this will be part of the consultation. Similarly, people with specific medical conditions or scalp disorders (especially automated immune diseases) may experience complications that can prevent transplantation success.
Non -relevant expectations
Patients often have unrealistic expectations of hair transplant results. This can lead to despair, and the notion that the bond has failed in a situation that is not necessarily. It is necessary for the surgeon to provide a complete explanation of what can and cannot be obtained. While hair transplantation can significantly improve the appearance, it does not restore the hair to its original density. Determining realistic goals and ensuring the patient’s understanding of the limitations of this method can prevent dissatisfaction. It is important to emphasize that unrealistic expectations, especially in younger patients – regardless of how much they are advised – are common – lead to a weak decision that may affect their entire lives.
Inadequate surgery expertise
The skill and experience of the surgeon are important determinants in hair transplantation. Inadequate surgical expertise can lead to poor transplantation, improper implantation angle and rough hair distribution, including others. This can lead to abnormal appearance or lack of transplanting hair. It is important to select a licensed surgeon from the extensive hair transplant board to minimize these risks.
Post -operation poor care
Postoperative care is as important as surgery. Patients must follow the post -surgery instructions provided by their surgeon to ensure optimal recovery and transplant survival. Failure to comply with these instructions can eliminate transplantation, infection or poor recovery, all of which can endanger the success of the transplant. Activities such as smoking, excessive physical pressure and improper scalp washing can also affect transplanted hair.
The condition of infection and scalp
Infections and conditions of the scalp can significantly affect the outcome of hair transplantation. Infections can be caused by poor surgical technique, insufficient sterilization or postoperative care. Scalp conditions such as psoriasis and dermatitis can also interfere with the care of the bonds. It is very important for patients to disclose their medical history and surgeons can eliminate any skin conditions before transplanting. Ensuring that your chosen physician is a licensed dermatologist can help identify possible scalp problems.
Sufficient blood supply
Success in hair transplantation relies heavily on blood -transplanted follicles. Adequate bleeding cannot lead to transplantation, where transplanted hair does not root or grow. Factors that can disrupt blood, including the construction of receptor sites (the hole in which the transplant is placed), make these sites very close or close. The pre -existing vascular conditions, such as the widespread sun damage and, of course, smoking cause growth or lead to complete hair transplant failure. Patients with blood disorders that increase coagulation, such as sickle cell disease, may be at particular risk. Surgeons should also guarantee minimal physical damage to the scalp during surgery. Cutting the donor area that is very tightly closed can also endanger blood flow to the scalp. Scalp necrosis is a severe condition, where the hair not only does not grow, but also parts of the scalp may also be eliminated and have an unpleasant scar.
Medications that increase bleeding
Anticoagulant, such as codin and plwix, can significantly increase bleeding and lead to transplantation from the receptor sites. It may also cause the blood to be compressed under the skin and the unwanted pressure may be applied to the above tissue.






